This blog post explains how to enable and configure advanced auditing for Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS), and how to collect and send the resulting logs to Microsoft Sentinel. By default, logging for ADCS is not enabled, which means you may miss important insights about your environment.
Please remember that you need to carry out the same activities on all ADCS servers.
Requirements for ADCS Auditing with Microsoft Sentinel
To successfully carry out ADCS auditing and log collection in Microsoft Sentinel, the following components are required:
- Azure Log Analytics workspace
- Microsoft Sentinel
- Azure Arc connected server
- Azure Monitoring Agent on Azure Arc connected servers
Why Azure Arc is Essential for Efficient ADCS Auditing
Even when using Defender for Cloud or Microsoft Sentinel for security event forwarding, Azure Arc plays a critical role. It enables the Windows Security Events via AMA connector in Microsoft Sentinel, allowing you to define custom Data Collection Rules. These rules can be set to varying levels – None, Minimal, Common, All Events, and Custom. The Custom setting is particularly beneficial for ADCS logs, as it allows for tailored xpath queries, ensuring precise data collection and optimizing costs.
The Common Events option only includes around 150 different events from the security log, and does not include specific ADCS event IDs. While you could set your Security Events connector or Defender for Cloud to forward all logs, this may not be desirable. Azure Arc and the Azure Monitoring Agent allow you to define your own Data Collector Rules and collect only the needed events.
ADCS auditing
The first step is ensuring auditing is enabled on your ADCS servers.
Using Auditpol utility
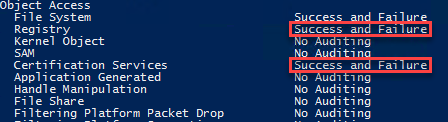
Run the auditpol command and ensure that “Certificate Services” and “Registry” advanced auditing are enabled.
auditpol /get /category:*
auditpol /set /subcategory:"Certification Services" /success:enable /failure:enable
auditpol /set /subcategory:"Registry" /success:enable /failure:enable
Using Group Policy
- Open Group Policy Management
- Create or Edit a Group Policy Object (GPO)
- Edit the GPO
- Right-click on the GPO you’ve created or chosen and select “Edit“
- Navigate to Advanced Audit Policy Configuration
- In the Group Policy Management Editor, go open the following Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Advanced Audit Policy Configuration -> Audit Policies.
- Configure “Certification Services” Auditing
- Navigate to Object Access.
- Find and double-click on “Certification Services“
- Check the boxes for “Configure the following audit events” and then check both “Success” and “Failure“
- Click OK
- Configure “Registry” Auditing
- Still under Object Access, find and double-click on “Registry“
- Check the boxes for “Configure the following audit events” and then check both “Success” and “Failure“
- Click OK
- Close the Group Policy Management Editor
- Assign the GPO to the PKI servers
ADCS Auditing Settings
The next step is to enable auditing through the ADCS snap-in. To do that, follow the steps on your ADCS server:
- Open Server Manager
- Select Tools -> Certification Authority
- Right-click your CA name and choose properties
- Select Auditing
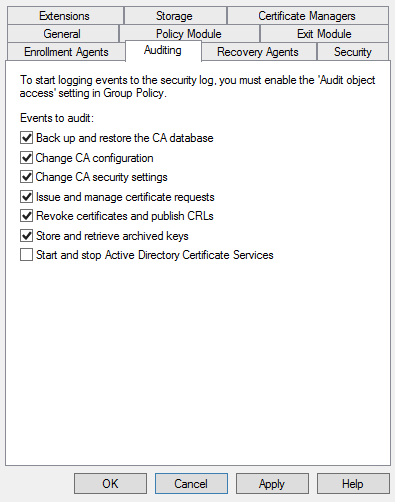
- Enable the auditing settings you need
- Back up and restore the CA database
- Change CA configuration
- Change CA security settings
- Issue and manage certificate requests
- Revoke certificates and publish CRLs
- Store and retrieve archived keys
- Start and stop ADCS service
Certificate Template Changes
The next step is to enable the certificate template changes using the certutil command:
certutil –setreg policy\EditFlags +EDITF_AUDITCERTTEMPLATELOAD
Extra Registry Auditing
Because some changes can be done directly through the registry, we need to enable registry auditing. To do that, we need to do this:
- Open Regedit on your ADCS server
- Browse the following key
- *HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\CertSvc\Configuration*
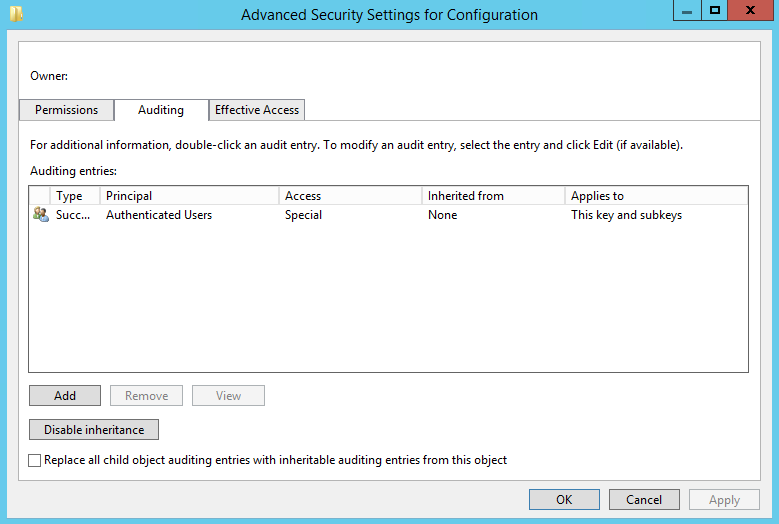
- Right-click Configuration and choose Permissions
- Click Advanced
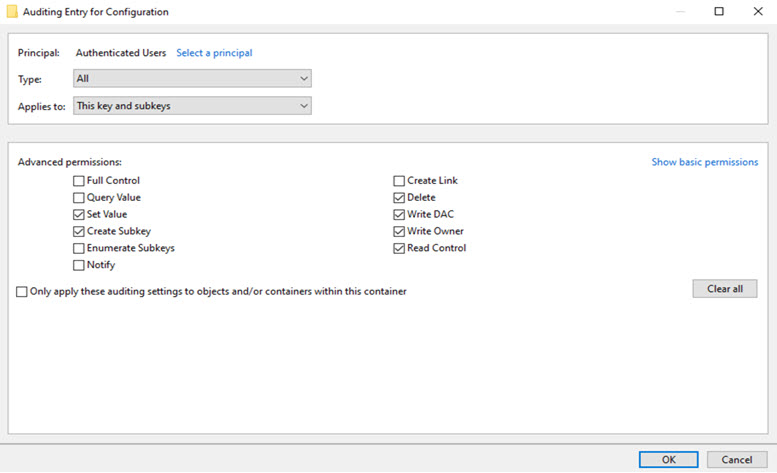
- Choose Auditing and click Add
- Set the principal to Authenticated Users and configure the following permissions
- Set Value
- Create SubKey
- Delete
- Write DAC
- Write Owner
- Read Control
Reboot your server and verify the changes. After the reboot, you should see different event IDs in your Security logs.
Defender for Identity
For those who have acquired Defender for Identity licenses, it’s important to install the Defender for Identity Sensor on your Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) Servers. This addition requires no extra licenses as it is already included in your Defender for Identity license. Furthermore, there is no need for additional sizing considerations. The installation process involves simply adding the sensor.
Maximizing Your Microsoft Secure Score for ADCS
As an MDI customer, installing the sensor unlocks tailored security recommendations. Ensure to review and implement these key actions to boost your Secure Score:
- Edit Misconfigured Certificate Templates ACL (ESC4)
- Rectify Misconfigured Enrollment Agent Certificate Template (ESC3)
- Restrict Overly Permissive Certificate Templates with Privileged EKU (ESC2)
- Correct Misconfigured Certificate Templates Owner (ESC4)
- Prevent Arbitrary Certificate Requests Based on Template (ESC1)
- Refine Misconfigured Certificate Authority ACL (ESC7)
- Amend Vulnerable Certificate Authority Settings (ESC6)
- Mandate Encryption for RPC Certificate Enrollment Interface (ESC8)
Implementing these measures will not only enhance your Secure Score but also fortify your ADCS environment.
Azure Arc configuration
For Azure Arc configuration, follow this guide – Connect hybrid machine with Azure Arc enabled servers – Azure Arc | Microsoft Docs
Insights from ADCS Event Logs
For a deeper dive into the specific events and activities within your ADCS environment, I have compiled detailed ADCS event logs. These logs provide critical insights into the operational health and security posture of your ADCS infrastructure.
To understand the nuances of these event logs and how they can inform your security strategy, refer to the detailed analysis in my dedicated post: Understanding Microsoft ADCS Services Event Logs.
Microsoft Sentinel
Now that you have Azure Arc up and running, we can continue with the Data Collection Rules. In Microsoft Sentinel, we have a connector called Windows Security Events via AMA. This connector allows us to define custom log policies for Azure Arc-enabled servers. In the Data Collector Rules, you need to specify the XPATH queries.
Security!*[System[(EventID=4882 or EventID=4899)]]
You can test your XPATH queries using the Get-WinEvent PowerShell cmdlet.