Introduction
There are several ways to connect machines to Azure Arc, including using the Microsoft Monitoring Agent, as I discussed in a previous blog post. However, not all customers use Azure Update Management, so alternative methods for onboarding Azure Arc agents may be needed. These alternative methods can help ensure that you can connect your machines to Azure Arc, regardless of whether they use Azure Update Management.
You can read more about how to do the onboarding through MMA and Azure Update Management.
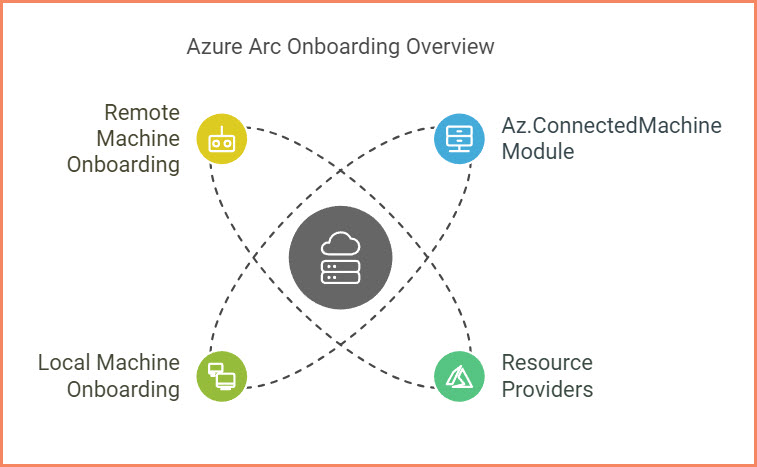
In this blog post, I will show how to use Az.ConnectedMachine PowerShell module to onboard machines to Azure Arc. The Az.ConnectedMachine module is an official module from Microsoft that provides a range of commands for managing and monitoring Azure Arc-connected machines. The current version (1.1.0) of the Az.ConnectedMachine module includes 35 different commands, which can be used to perform a wide variety of tasks related to Azure Arc-connected machines.
Az.ConnectedMachine module commands:
Connect-AzConnectedMachine
Get-AzConnectedExtensionMetadata
Get-AzConnectedLicense
Get-AzConnectedLicenseProfile
Get-AzConnectedMachine
Get-AzConnectedMachineExtension
Get-AzConnectedMachineRunCommand
Get-AzConnectedNetworkSecurityPerimeterConfiguration
Get-AzConnectedPrivateLinkScope
Install-AzConnectedMachinePatch
Invoke-AzConnectedAssessMachinePatch
Invoke-AzConnectedReconcileNetworkSecurityPerimeterConfiguration
New-AzConnectedLicense
New-AzConnectedLicenseDetail
New-AzConnectedLicenseProfile
New-AzConnectedLicenseProfileFeature
New-AzConnectedMachineExtension
New-AzConnectedMachineRunCommand
New-AzConnectedPrivateLinkScope
Remove-AzConnectedLicense
Remove-AzConnectedLicenseProfile
Remove-AzConnectedMachine
Remove-AzConnectedMachineExtension
Remove-AzConnectedMachineRunCommand
Remove-AzConnectedPrivateLinkScope
Set-AzConnectedLicense
Set-AzConnectedMachineExtension
Set-AzConnectedPrivateLinkScope
Update-AzConnectedExtension
Update-AzConnectedLicenseProfile
Update-AzConnectedLicenseProfileFeature
Update-AzConnectedMachine
Update-AzConnectedMachineExtension
Update-AzConnectedMachineRunCommand
Update-AzConnectedPrivateLinkScopeTag
How to install Az.ConnectedMachine PowerShell module
You can install the Az.ConnectedMachine PowerShell module directly from the PowerShell console. For the module installation, use the following command:
Install-Module -Name Az.ConnectedMachine -Verbose -Force
Required Azure Resource Providers
Before connecting machines to Azure Arc, you need to register the following resource providers at the subscription level:
Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.HybridCompute
Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.GuestConfiguration
Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.HybridConnectivity
Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.AzureArcData
Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.Compute
These registrations are required to enable the necessary Azure Arc functionalities for your on-premises or remote machines.
How to onboard local machine
- Open PowerShell as an administrator
- Execute the Connect-AzAccount command to connect to Azure
- Change the Subscription if needed using the Set-AzContext command
- Run the following command to onboard the local machine to Azure Arc:
$OnboardingDetails = @{
ResourceGroupName = "RG-PROD-IT-ARC"
Name = $env:COMPUTERNAME.ToUpper()
Location = "West Europe"
}
Connect-AzConnectedMachine @OnboardingDetail
If you have a lot of subscriptions, then you can also use the -SubscriptionId parameter in Connect-AzConnectedMachine, which doesn’t require a context change before onboarding.
How to onboard a remote machine
- Open PowerShell as an administrator
- Execute the Connect-AzAccount command to connect to Azure
- Change the Subscription if needed using the Set-AzContext command
- Create a new PowerShell Remoting session against the remote machine using the New-PSSession command
- Run the following command to onboard the remote machine to Azure Arc
$ServerName = "SERVER02"
$PSRemoteSession = New-PSSession -ComputerName $ServerName
$OnboardingDetails = @{
ResourceGroupName = "RG-PROD-IT-ARC"
Location = "West Europe"
PSSession = $PSRemoteSession
}
Connect-AzConnectedMachine @OnboardingDetails
You can also create multiple remote sessions against many machines, and you can onboard many machines at the same time.
Conclusion
Connecting machines to Azure Arc doesn’t have to be a complex process. With the Az.ConnectedMachine PowerShell module, you can easily onboard machines to Azure Arc, regardless of whether they’re local or remote. So why wait? Start leveraging the power of Azure Arc today!