Introduction
In the evolving landscape of digital identity management, Microsoft Entra ID has introduced a robust feature known as Restricted Management Administrative Units. They allow for the segregation of administrative powers, ensuring that only a designated set of administrators can modify specific objects within the tenant. This arrangement is critical for protecting sensitive accounts and devices, meeting stringent compliance requirements, and maintaining a high level of organizational security.
Building on the foundational insights from my previous post, this article delves into a more dynamic aspect of Restricted Management Administrative Units: the creation and management of dynamic device Restricted Admin units. The focus here is not just on the what and why but also on the how – specifically, visualizing the process of setting up these units with members automatically pulled from specified groups. This approach simplifies the traditionally manual and time-consuming task of managing member lists in administrative units, offering a streamlined and efficient solution for modern administrators.
Dynamic Device Restricted Admin Units
Dynamic management of Restricted Management Administrative Units in Microsoft Entra ID is critical for securing and managing sensitive assets. It streamlines the management of Secure Access Workstation (SAW) devices, cloud administrator accounts, break glass accounts, and sensitive groups across Entra ID, Intune, and Defender for Endpoint ecosystems. This automation ensures assets are always in the correct administrative units, reducing manual workload and maintaining security through immediate updates to access controls based on changes in status or role.
Simplifying Membership Management of Sensitive Assets
- Automated Updates: Dynamic management automates the process of updating membership lists. For sensitive assets like SAW devices or high-privilege accounts, this means that any changes in status or role are immediately reflected in the administrative units, without manual intervention.
- Consistency and Accuracy: Automation reduces the risk of human error, ensuring that only the appropriate devices and accounts are part of the sensitive units. This consistency is crucial when dealing with assets that, if mismanaged, could expose the organization to significant risks.
Enhancing Security of Critical Resources
- Targeted Control: By dynamically managing these units, organizations can exert more granular control over who has access to critical resources like cloud administrator accounts and break glass accounts.
- Reduced Attack Surface: Limiting access to sensitive groups and accounts through dynamic management minimizes the attack surface, making it harder for unauthorized users to gain access to critical systems or data.
Effective Use Cases
- Secure Access Workstation (SAW) Devices: For devices used in high-security contexts, dynamic management ensures that only those devices meeting strict criteria (like being part of a specific security group) are managed within a tightly controlled administrative unit.
- Cloud Administrator Accounts: Dynamic management can automatically segregate these accounts into a restricted unit, ensuring that only a select group of senior administrators have the authority to manage these high-privilege accounts.
- Break Glass Accounts: These emergency accounts, used for bypassing standard authentication processes in crisis scenarios, can be dynamically managed to ensure they remain secure and accessible only to a few key personnel.
- Sensitive Groups in Entra ID, Intune, or Defender for Endpoint: Groups that control access to critical applications or data can be dynamically managed to automatically update membership, ensuring that only current, authorized personnel have access.
By focusing on the dynamic management of Restricted Management Administrative Units for these sensitive assets, organizations can achieve a higher level of security and efficiency. This approach is essential in a landscape where the quick and secure management of critical resources is not just a convenience, but a necessity for maintaining operational integrity and compliance.
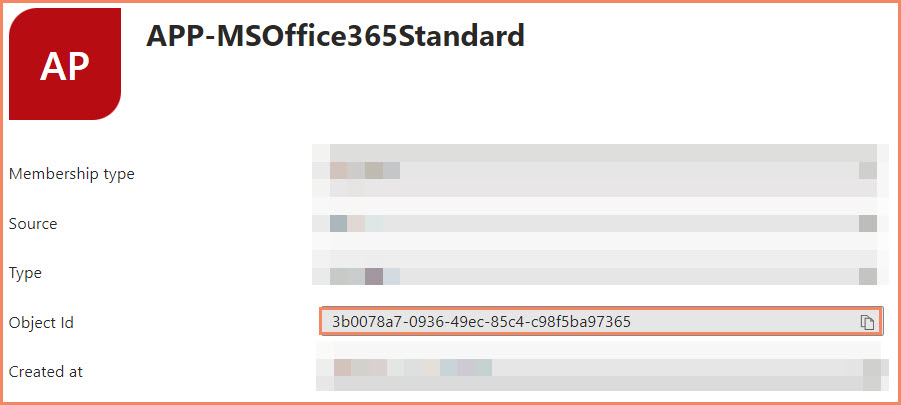
Group ID Identification
Identifying and correctly inputting the necessary GROUP IDs is a critical step in setting up dynamic device membership for Restricted Management Administrative Units in Microsoft Entra ID. This process ensures that your dynamic query accurately reflects the groups whose members should be automatically included in the administrative unit.
Copy and paste the Object ID and use that in the Dynamic Query.
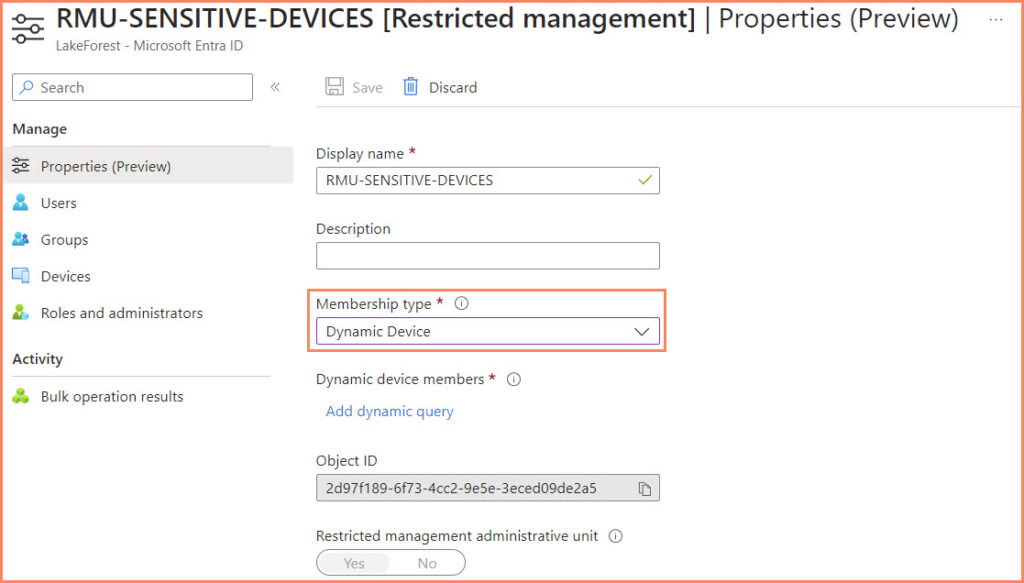
Creating a Restricted Management Administrative Unit
Creating a Restricted Management Administrative Unit in Microsoft Entra ID, particularly with dynamic device membership, involves a sequence of steps. This process ensures that your administrative units are precisely tailored to meet the specific needs of your organization. Here’s how to go about it:
- Accessing Microsoft Entra ID
- Navigating to Administrative Units
- Creating a New Administrative Unit
- Enabling Restricted Management
- Setting the Membership Type to Dynamic Device
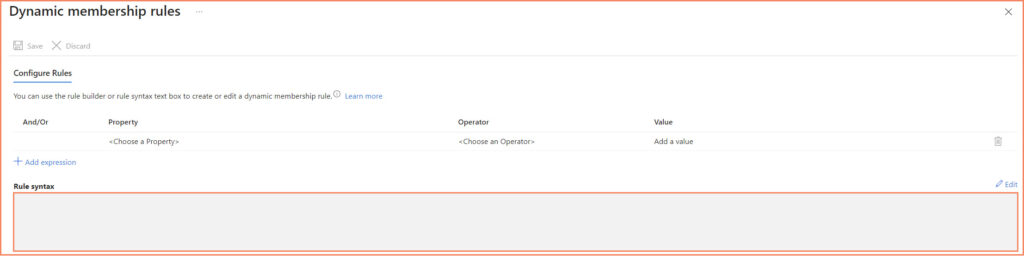
- Specifying the Dynamic Membership Rule
- Implementing the Dynamic Query
- Saving and Verifying
device.memberof -any (group.objectId -in ['XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXX'])
Delegating Permissions
Delegating permissions within Restricted Management Administrative Units is a crucial aspect of maintaining secure and efficient management of organizational assets. This delegation ensures that the right individuals have the appropriate level of control and access, aligning with the principle of least privilege. Here’s an explanation of why and how this is important:
- Ensuring Security and Compliance: By carefully delegating permissions, you can limit access to sensitive assets, such as executive devices or confidential data, to a select group of administrators. This restricted access is essential for complying with various security standards and regulations, which often mandate strict control over who can manage critical assets.
- Aligning with the Principle of Least Privilege: The principle of least privilege dictates that users should be granted only the access necessary to perform their job functions. In the context of Restricted Management Administrative Units, this means assigning only the necessary permissions to administrators responsible for managing specific units. This approach minimizes potential security risks associated with excessive privileges.
- Streamlining Management: Delegating permissions allows for more efficient management of assets. Administrators with clearly defined roles and responsibilities can focus on their specific areas without interference. This clear division of duties can lead to quicker resolution of issues and more organized management practices.
Delegating permissions in this manner not only enhances the security posture of your organization but also ensures a more streamlined and focused administrative approach. By doing so, you maintain control over your assets while allowing for flexibility and scalability in management practices.
Automation
If you want to automate your activities around the Restricted Administrative Units, I recommend reading this article on automating Restricted Administrative Units.
KQL Queries
For those interested in exploring Azure Active Directory’s Restricted Management Administrative Units using KQL, check out this insightful guide on KQL.
Conclusion
Implementing Dynamic Device Restricted Management Administrative Units in Microsoft Entra ID is a crucial strategy for enhancing security and efficiency in managing sensitive organizational assets. Throughout this guide, we have explored the process of creating these units, highlighting their importance in today’s cybersecurity environment and detailing the steps involved in managing memberships dynamically.
This dynamic management approach streamlines the often complex and time-consuming task of manual membership updates, significantly boosting operational efficiency and security. By automating the inclusion of specific devices and accounts, such as Secure Access Workstation devices, cloud administrator accounts, and sensitive groups, organizations can maintain a robust and adaptive security posture.
The ability to modify membership types after creation offers flexibility, enabling organizations to respond effectively to changing needs and circumstances. Careful delegation of permissions within these units ensures that critical resources are managed by appropriately authorized personnel, adhering to the principle of least privilege and reducing security risks.
As digital security becomes increasingly vital, understanding and implementing Restricted Management Administrative Units in Microsoft Entra ID is essential for safeguarding an organization’s most critical assets. This guide lays the groundwork for deeper engagement with these practices, ensuring that your organization remains secure and agile amidst the dynamic challenges of the digital landscape.